Komisja Europejska przedstawiła Strategiczny dialog na temat przyszłości rolnictwa w UE. Sam dialog został zapowiedziany przez przewodniczącą Ursulę von der Leyen w orędziu o stanie Unii w 2023 r. Jego celem było wypracowanie wspólnej wizji przyszłego unijnego systemu rolnego i żywnościowego przez kluczowych interesariuszy z całego łańcucha rolno-spożywczego, w tym rolników, kooperatywy, przedsiębiorstwa spożywcze, społeczności wiejskie, organizacje pozarządowe, przedstawicieli społeczeństwa obywatelskiego, instytucje finansowe i akademickie.
Raport z dnia: 05/09/2024
16/09/2024
European Union [EU]
110
angielski
PREFACE BY THE CHAIR 4
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 8
PART A : FUTURE AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SYSTEMS IN THE EUROPEAN UNION 16
1. Food production, a central function in modern societies 17
2. Changing and challenging contexts 19
3. A vision for the future 21
PART B: GUIDING POLITICAL PRINCIPLES 26
PART C: RECOMMENDATIONS 36
C.1.: Working together for a sustainable and competitive future 37
1.1. A fair and competitive food value chain 37
1.1.1. Strengthening farmers’ position in the food value chain 37
1.1.2. Competitiveness and sustainability ofthe food value chain 39
1.2. A new approach to deliver on sustainability 40
1.3. Preparing a Common Agricultural Policy ft for purpose 42
1.3.1. Socio-economic support to farmers: 43
1.3.2. Environmental and animal welfare outcomes: 43
1.3.3. Process of transforming the CAP: 44
1.4. Financing the transition 45
1.5. Promoting the global transition 47
1.5.1. Coherence between trade policy and sustainability requirements 47
1.5.2. EU’s trade agreement approach 49
1.5.3. The global trade policy framework 50
1.6. Policy framework and governance 50
1.6.1. A European board on agri-food (EBAF) 51
1.6.2. Policymaking and simplifcation 52
C.2. Advancing towards sustainable food systems 54
2.1. Making the healthy and sustainable choice the easy one 54
2.1.1. Empowering consumers 55
2.1.2. Public procurement 56
2.2. Enhancing sustainable farming practices 57
2.2.1. Reducing GHG emissions in agriculture and food systems 57
2.2.2. Soil management, biodiversity, fertilisation and circularity 61
2.2.3. Organic farming 63
2.2.4. Agroecological solutions 63
2.3. Creating pathways for sustainable animal farming in the EU 64
2.3.1. Sustainable transition 65
2.3.2. Animal welfare legislation 66
2.3.3. Animal welfare labelling 67
2.4. Leveraging the opportunities ofered by bioeconomy 67
2.5. Towards a zero-waste future and responsible usage of food surpluses 68
C.3: Promoting transformative resilience 70
3.1. Better preserving and managing farmland 70
3.1.1. Nonet land take by 2050 71
3.1.2. European Observatory for Agricultural Land 71
3.2. Scaling up adaptation 72
3.2.1. Water-resilient agriculture 72
3.2.2. Innovative plant breeding approaches 73
3.3. Robust risk and crisis management 74
C.4. Building an attractive and diverse sector 76
4.1. Supporting future generations of farmers 76
4.2. Attracting and protecting workers 78
4.3. Gender equality and diversity 80
4.4. Invigorating rural communities 81
C.5. Better access to and use of knowledge and innovation 84
5.1. Facilitating access to and better sharing of knowledge and skills 84
5.2. Increasing investments and partnerships in Research & Innovation 85
5.3. Streamlining regulatory procedures for the access to market of new technologies and innovations 86
5.4. Using the opportunities of digitalization in a responsible manner 86
5.5. Social Innovation as an enabler of sustainable farming 87
CONCLUSION 88
ANNEX 90
1. Mandate 91
2. Members of the Strategic Dialogue on the Future of EU Agriculture 92
3. Rules of Procedure 94
4. Timetable of the Strategic Dialogue on the Future of EU Agriculture 96
5. European Investment Bank Group contribution to the fnal report 98
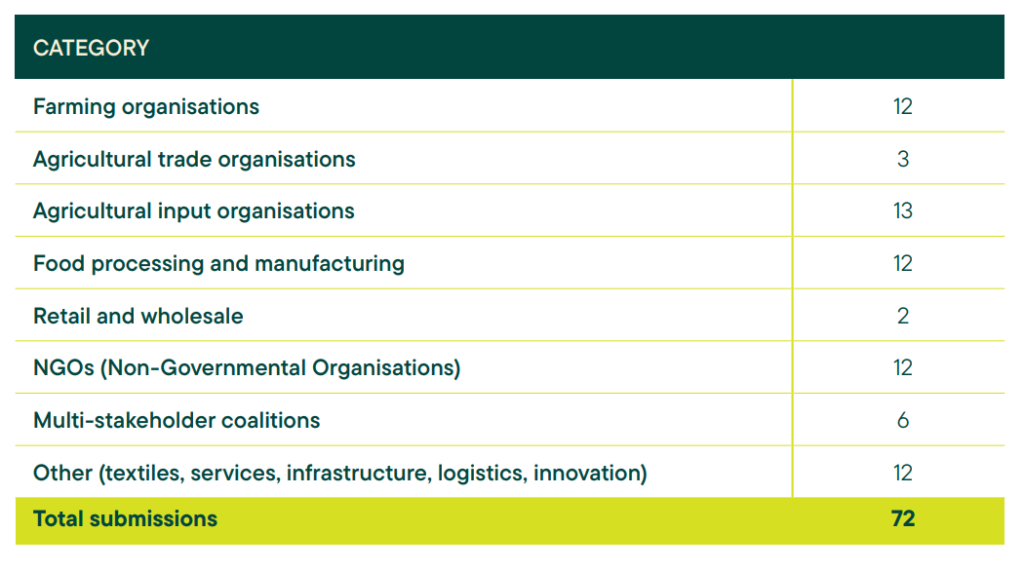
6. Synthesis of the targeted consultation 101
7. Abbreviations 106
Uczestnicy dialogu strategicznego na temat przyszłości rolnictwa UE